AMD Ryzen Threadripper 9000 Series processors just launched, and it’s quite possible that you have a pile of questions about these high-end chips. What makes them special? Who are they for? What kind of hardware do you need to run one? To catch you up to speed, we’ve put together this beginner-friendly FAQ.
What is a workstation?
Speaking generically, a “workstation” is simply a PC used for doing work, though you wouldn’t use the word to describe a machine capable of little more than sending emails. More specifically, a workstation is a desktop PC that’s equipped for advanced processing capabilities above and beyond what you can get with the consumer-grade hardware that you find in standard PCs and laptops.
What are the differences between a standard PC and a workstation?
The differences between standard PCs and workstations vary depending on the hardware that you’re comparing, but these elements are common, if not essential:
- High-end desktop (HEDT) processor support. Workstations support CPUs with a much higher core count than is available through standard PC hardware.
- Advanced memory architectures, including ECC. Workstations typically offer quad-channel or even eight-channel memory configurations for greatly increased bandwidth, while also supporting Error Correction Code (ECC) memory, which is vital for use cases where data integrity and system stability are critical.
- Increased expansion slot options. Workstation users often increase the capabilities of their machines through multiple add-in boards. An increased number of PCIe x16 slots allows for multiple GPU configurations at full PCIe bandwidth.
- Remote management support. Many, but not all workstations give businesses the hardware tools they need to service and update PCs remotely.
- Price. The higher-end components for a workstation PC are more expensive due to their specialized hardware and any certifications.
What kinds of PC users require workstation-class hardware?
Workstations are typically used in professional contexts, though certain types of PC enthusiasts and power users find use in their homes for this advanced hardware. Workstations offer a clear performance advantage over standard PCs when it comes to professional content creation, video editing, scientific research, engineering, architecture, and 3D/CAD modeling. Some software developers and programmers also have workflows which are greatly accelerated by the specialized hardware of a workstation.
What is an AMD Ryzen Threadripper processor?
If you’ve built a desktop PC recently, or purchased a laptop or prebuilt desktop, you likely know of the company AMD, one of the world’s premier designs of CPUs. The company’s Ryzen line is a popular choice in many contexts.
AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors are a separate line. While there are similarities in the architecture between AMD Ryzen and AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors, they install into different CPU sockets and serve different classes of users. While AMD Ryzen chips are targeted at the general consumer PC market, AMD Ryzen Threadripper CPUs are designed for workstation PCs. AMD EPYC processors are designed for the server market.
Is an AMD Ryzen Threadripper processor worth it?
AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors do carry a significant price premium over AMD Ryzen chips, with the top-end chip typically costing many thousands of dollars. They’re usually purchased for professional contexts in which their advanced capabilities will accelerate workflows to such an extent that their users can expect a significant return on their investment. For example, if a workstation with an AMD Ryzen Threadripper processor can help your video editing business export completed projects at a much faster rate than your current hardware, then a Threadripper CPU is absolutely worth it.
However, not all applications benefit equally from having access to the extremely high core counts offered by AMD Ryzen Threadripper CPUs. Modern PC games, for example, are almost never optimized to take advantage of that many CPU cores. Gamers will typically not see a benefit from upgrading from an AMD Ryzen CPU to an AMD Ryzen Threadripper CPU, and should look at options in the AMD Ryzen lineup.
What are the differences between standard AMD Ryzen processors and AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors?
AMD Ryzen processors are built for the general PC market. AMD Ryzen CPUs appear in a wide range of laptops and PCs, including general-use machines for everyday computing. Some high-end chips in the series, such as the AMD Ryzen 7 9800X3D, offer specialized features that accelerate gaming, including AMD 3D V-Cache Technology. AMD Ryzen CPUs are known for offering plentiful CPU cores and threads to better support multitasking, highly parallel operations, and advanced PC workflows. The top-end Ryzen 9 9950X3D offers 16 cores and 32 threads for powerful multithreaded performance, while also offering a max boost clock of up to 5.7GHz for nimble performance in lightly threaded workloads.
AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors support advanced PC use cases through their exceptionally high core count. The most affordable of the latest AMD Ryzen Threadripper 9000 Series CPUs offers 24 cores and 48 threads, and the top-end model is equipped with 96 cores and 192 threads.
What hardware do I need for a complete workstation PC build?
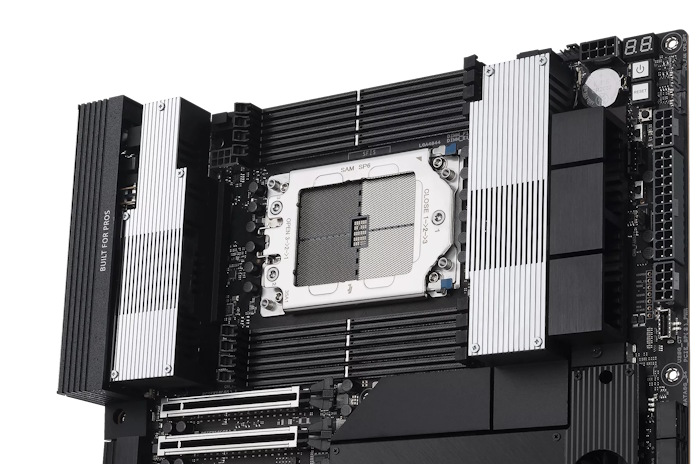
Your workstation PC build starts with a workstation-class CPU like an AMD Ryzen Threadripper 9000 Series CPU. Pair it with a motherboard with the appropriate CPU socket — sTR5, if you’re installing one of the latest Threadrippers. As you’re selecting a motherboard, consider your needs for the complete build. How much memory will you install? How many expansion slots do you need? What are your needs for networking and USB connectivity? Will you be overclocking this system? Your motherboard will set the possibilities for these elements of the platform.
Typically, workstation motherboards are larger than standard motherboards. Pay close attention to the form factor and select a PC case that offers out-of-the-box compatibility for an easy building experience. A workstation PC can draw a substantial amount of power, especially if you install multiple graphics cards. An ASUS Pro WS Platinum Series PSU will give you the high-end wattage that you might need in a compact design that’s easy to install.